In the past decade, the integration of radiological electronic data has skyrocketed, leading to a growing need for secure storage and efficient backup of large volumes of imaging data. As healthcare systems move towards digital solutions, cloud technology has become the cornerstone for handling this vast data influx. The transition to cloud computing in radiology is not merely a trend, but a necessary evolution, particularly in handling the immense storage requirements and enhancing accessibility to medical data.
What is Cloud Technology?
Cloud computing, in essence, refers to the on-demand delivery of computing services, including storage, servers, networking, and applications, via the internet. Unlike traditional methods, where organizations maintain their own data infrastructure, cloud technology allows for scalable, flexible, and efficient access to shared resources. This setup enables organizations to eliminate the need for substantial upfront capital investments in hardware and reduces long-term maintenance costs. For healthcare systems, this translates to a cost-effective way to store and manage large radiological datasets.
One of the main advantages of cloud technology is the flexibility it offers through models like Software as a Service (SaaS), where storage and computational tasks are handled off-site. In radiology, this facilitates the storage and remote processing of medical imaging data, such as CT and MRI scans, without requiring significant investment in on-site infrastructure. The cloud can even support more complex processes, like 3D renderings or advanced imaging reconstructions, performed on remote servers and displayed on mobile devices.
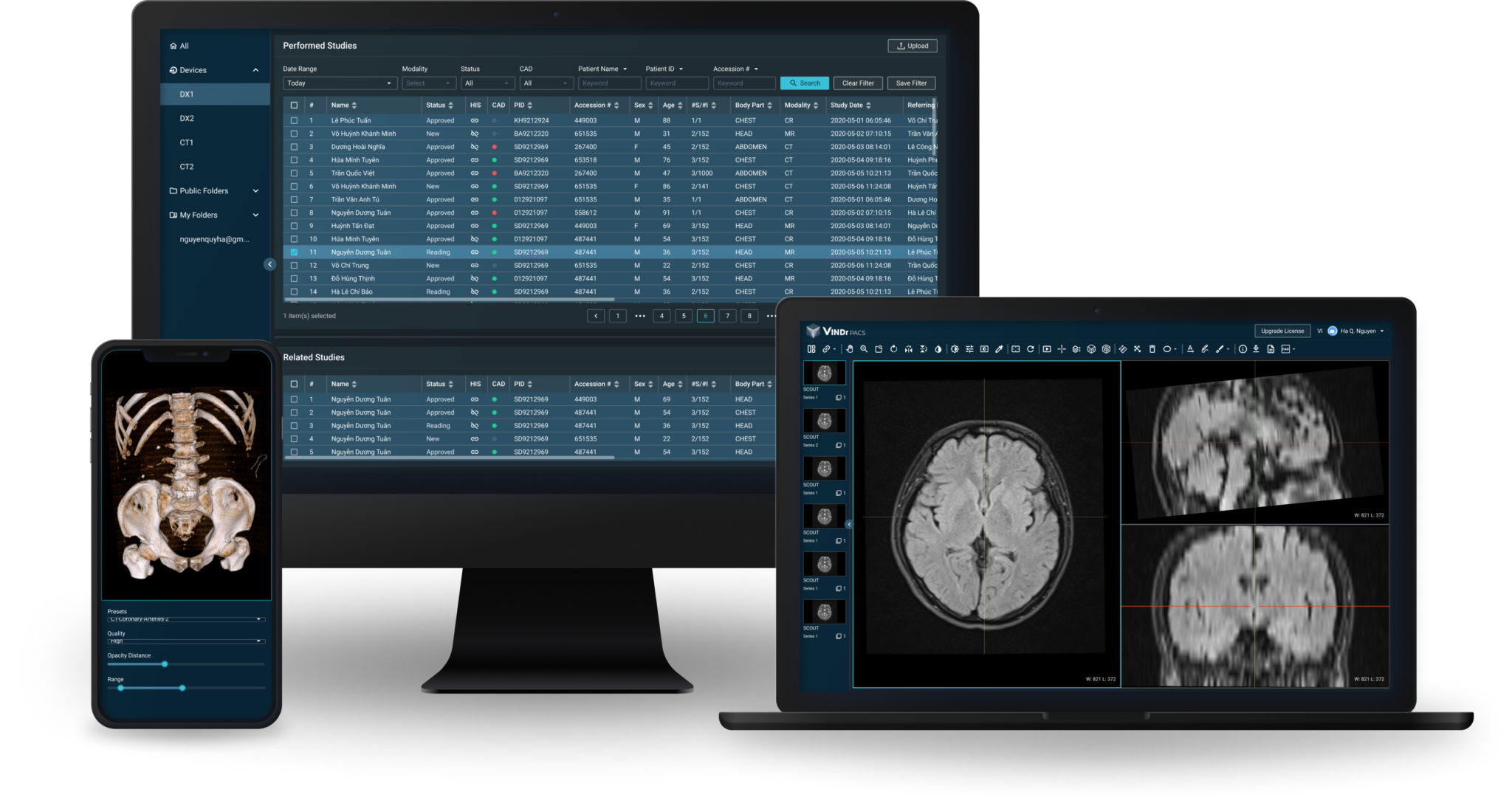
The Role of Cloud Technology in Radiology
The application of cloud computing in radiology is revolutionizing how imaging data is stored, accessed, and shared. For hospitals and radiologists, the cloud offers a centralized platform to store medical images and radiology reports, eliminating the need for physical transfer and storage of large datasets on local servers. This ensures smoother sharing of images across institutions, making it easier to collaborate and seek second opinions without the logistical barriers that traditionally existed.
In addition, cloud-based solutions provide a seamless way for patients to access their imaging records and share them with healthcare providers, improving the coordination of care. This reduces redundancy in diagnostic tests, accelerates diagnosis, and supports better clinical outcomes. Furthermore, cloud technology enables radiologists to access previous imaging studies remotely, helping with comparative analysis and offering a more holistic view of a patient’s medical history.
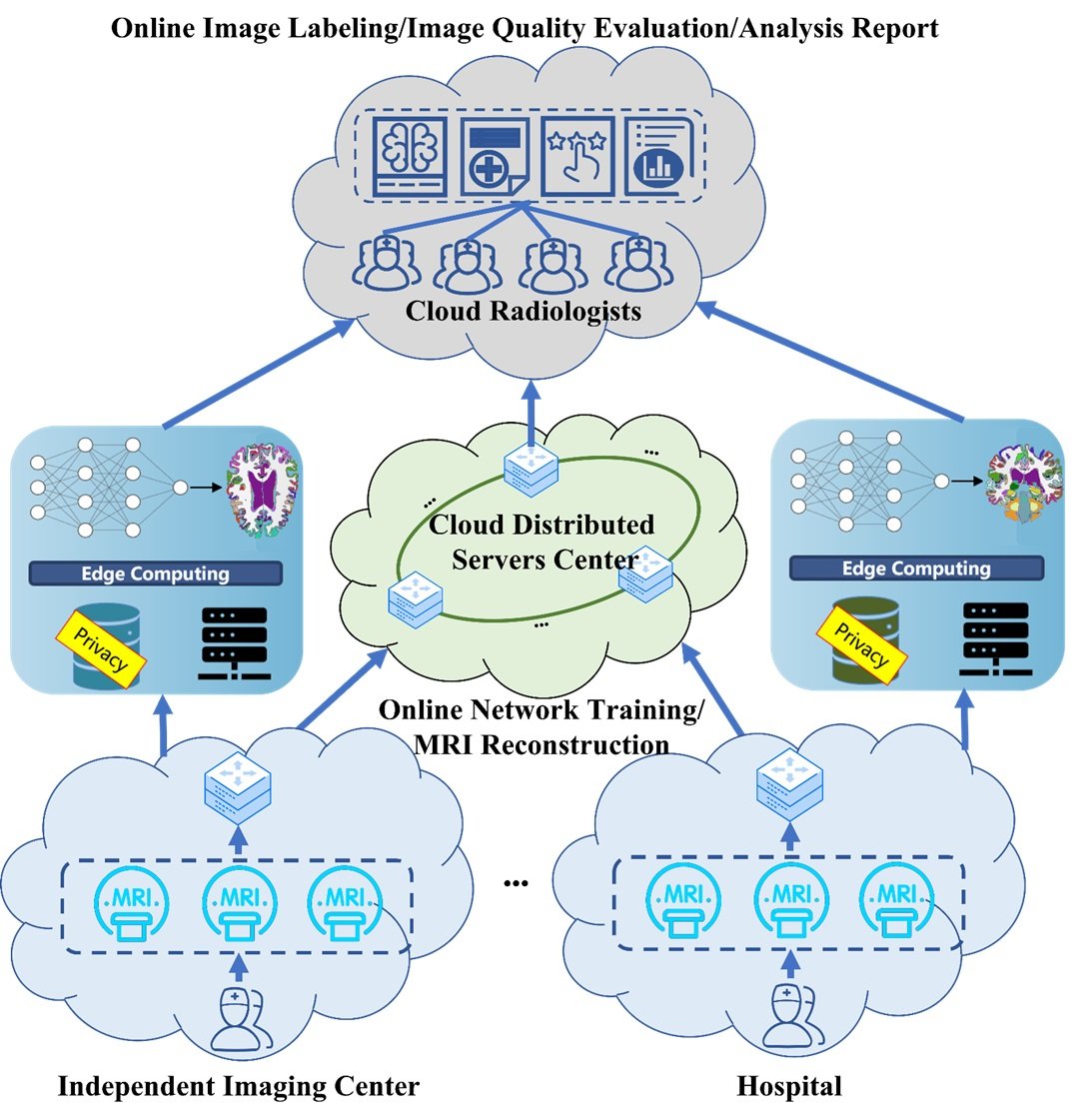
Data Security and Compliance: Navigating HIPAA in the Cloud
For cloud solutions to be viable in healthcare, data privacy and security are of utmost importance. Regulatory frameworks such as HIPAA in the United States demand strict standards for safeguarding patient information. Cloud providers must meet these requirements by offering encrypted data transmission, secure storage solutions, and robust access controls.
In the case of radiology, where patient data is particularly sensitive, HIPAA compliance is non-negotiable. Cloud services typically utilize private clouds to ensure only authorized healthcare professionals have access to imaging data, minimizing risks associated with data breaches. Additionally, cloud services often include built-in disaster recovery protocols and security audits to ensure data integrity and mitigate the impact of potential outages.
Conclusion: The Future of Radiology in the Cloud
As cloud technology continues to mature, its role in healthcare—especially in radiology—becomes increasingly critical. The shift from traditional data storage systems to cloud-based solutions is not just about improving storage capacity; it is about transforming how medical imaging data is accessed, analyzed, and shared. With enhanced collaboration, improved security, and significant cost savings, the future of radiology is firmly rooted in cloud computing. Moving forward, it will be essential for healthcare organizations to carefully select cloud providers that meet their needs in terms of security, compliance, and uptime, ensuring that patient data remains protected while driving innovation in patient care.

References:
- Gerard P, Kapadia N, Chang PT, Acharya J, Seiler M, Lefkovitz Z. Extended outlook: description, utilization, and daily applications of cloud technology in radiology. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013 Dec;201(6):W809-11. doi: 10.2214/AJR.12.9673. PMID: 24261387.